AC Charging vs DC Charging: What’s the Real Difference?
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue gaining popularity, understanding efficient charging methods is essential for EV owners and businesses investing in charging infrastructure. Over 80% of EV owners use AC power at home, while DC fast charging is mostly used for long trips. (learn more) This leads to an important question: what are the key differences between AC charging and DC charging? This guide breaks down the technical aspects, advantages, and best use cases of both charging types, helping you decide on the best charging solution for your needs.
Understanding AC Charging
What is AC Charging?
AC (Alternating Current) charging is the most common and widely accessible method for charging electric vehicles. It uses the standard power supply available in homes and commercial buildings. Since EV batteries store energy in direct current (DC) form, the vehicle itself must convert AC to DC using an onboard charger before storing the energy.
How AC Charging Works
- The power from an AC charger passes through the EV’s onboard charger, which converts it into DC power before it reaches the battery.
- The charging speed depends on the vehicle’s onboard charger capacity and the power level of the AC charger.
Pros and Cons of AC Charging
Pros:
- More affordable to install and widely available.
- Suitable for home charging, workplace charging, and overnight charging.
- Gentler on the battery, helping to preserve long-term battery health.
Cons:
- Slower charging speeds compared to DC fast charging.
- Charging time varies significantly depending on the power level of the AC charger.
Best Use Cases for AC Charging
AC charging is ideal for daily charging routines, such as charging at home or the workplace. Tayniu’s portable EV chargers provide an excellent solution for users who need a flexible and reliable home charging setup, ensuring their vehicle is charged overnight and ready to go the next day.
Understanding DC Charging
What is DC Charging?
DC (Direct Current) charging, commonly known as fast charging, bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger, delivering DC power directly to the battery for quicker replenishment. This allows for much higher power delivery, significantly reducing charging time.
How DC Fast Charging Works
- Unlike AC charging, DC charging stations handle the AC to DC conversion before delivering energy directly to the EV battery.
- The power output varies widely, ranging from 50kW to 350kW, depending on the station and vehicle capabilities.
Pros and Cons of DC Charging
Pros:
- Much faster charging times compared to AC charging.
- Essential for long-distance travel and fleet operations.
Cons:
- More expensive to install and operate due to high power demands.
- Frequent use can accelerate battery degradation over time.
Best Use Cases for DC Charging
DC charging is best suited for public charging stations, highway rest stops, and commercial fleet operations. Tayniu’s commercial DC fast chargers provide high-efficiency solutions for businesses looking to offer fast charging services to EV drivers.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Charging
Charging Speed Comparison
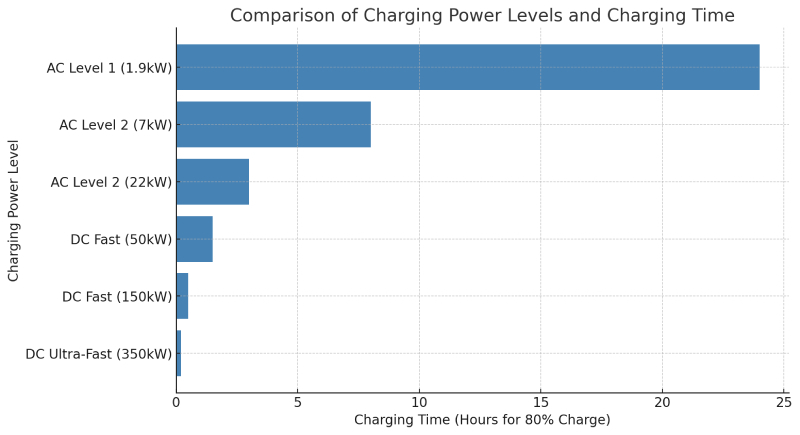
| Charging Type | Power Level | Approximate Charging Time (80% Charge) |
|---|---|---|
| AC Level 1 | 1.4kW–1.9kW | 8–24 hours |
| AC Level 2 | 3.3kW–22kW | 3–8 hours |
| DC Fast Charging | 50kW–350kW | 15–45 minutes |
Infrastructure and Cost Differences
- AC chargers are more affordable and easier to install, making them ideal for home use.
- DC chargers require higher infrastructure investment and a dedicated power supply, which makes them suitable for commercial applications.
Impact on EV Battery Life
- AC charging is slower but gentler on the battery, making it ideal for long-term battery health.
- DC charging is faster, but frequent use can contribute to faster battery degradation.
How to Choose the Right Charging Option
When deciding between AC charging vs DC charging, consider your daily driving habits, charging convenience, and infrastructure availability.
- Home Charging: If you primarily charge at home, an AC home charging station is the most cost-effective and battery-friendly solution. Tayniu’s home charging stations provide stable and efficient charging, ensuring your EV is ready for everyday use.
- Public and Business Charging: For businesses looking to offer charging services, commercial DC fast chargers are the best option to serve customers who need quick top-ups.
- On-the-Go Charging: If you need flexible charging locations, Tayniu’s portable EV chargers allow you to charge anywhere with an AC outlet.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between AC charging and DC charging is crucial for optimizing your EV charging experience. If you primarily charge at home or overnight, AC charging is the best option for cost-effectiveness and battery longevity. However, if you frequently take long trips or require rapid charging, DC fast charging is the better choice for minimizing downtime. While AC charging is best for regular home and long-term battery health, DC charging is necessary for fast, high-power charging.
Tayniu’s innovative EV charging solutions, including portable chargers, home stations, and commercial DC chargers, ensure that both individuals and businesses can find the perfect charging solution for their needs.
As EV adoption grows, choosing the right charging solution will enhance convenience, efficiency, and sustainability. Which type of charger best suits your lifestyle? Contact us to discuss your EV charging needs and find the best solution for you.
Last Updated on February 12, 2025 by tayniu