How EV Technologies Are Transforming the Auto Industry – What’s Next?
The Role of EV Technologies in Automotive Evolution
Electric vehicle (EV) technologies have been at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future of transportation. From early prototypes in the 19th century to today’s high-performance EVs with cutting-edge charging solutions, the evolution of EV technologies has been nothing short of revolutionary. In this article, we explore the history, advancements, and future trends of EV technology.
1. Early EV Technologies (1830s – 1900s)
The First Electric Vehicles
The first known EV was built in the 1830s by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson, utilizing crude non-rechargeable batteries. By the late 19th century, rechargeable lead-acid batteries enabled longer travel distances, leading to the rise of early commercial electric cars.
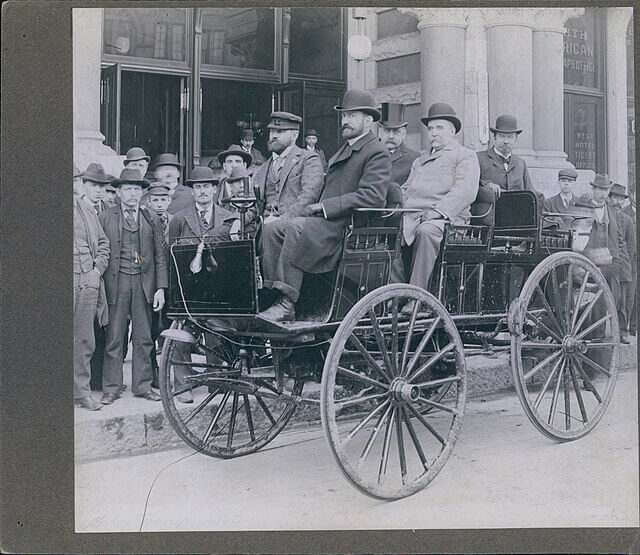

Electric car built by Thomas Parker in 1895. Source: Wikimedia Commons
EVs vs. Internal Combustion Engines (ICEs)
In the early 1900s, EVs had a competitive edge over gasoline-powered vehicles due to their quiet operation, ease of use, and lack of exhaust emissions. Brands like Baker Electric and Detroit Electric were pioneering the industry.
Charging Technologies in Early EVs
During this period, charging technology was rudimentary. EV owners had to rely on home charging from basic electrical outlets, which was slow and inefficient.
2. The Decline of EV Technologies (1900s – 1990s)
Despite their early popularity, EVs gradually lost market share to gasoline cars due to advancements in ICE technology, the mass production of gasoline vehicles by Ford (e.g., Model T), and the discovery of abundant fossil fuel resources.
Why EVs Lost the Race
- Limited Range: Early batteries could only sustain short trips.
- Long Charging Times: Charging infrastructure was nearly nonexistent.
- Advancements in ICE Technology: Gasoline cars became faster, cheaper, and had longer driving ranges.
By the mid-20th century, EV technology was largely forgotten, with only a few experimental projects keeping the concept alive.
3. The Revival of EV Technologies (1990s – Present)
The Lithium-Ion Battery Revolution
The development of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s marked a turning point. Compared to lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, lithium-ion technology provided:
- Higher energy density (longer range per charge)
- Faster charging times
- Lighter weight
Tesla and the Modern EV Boom
Tesla’s introduction of the Roadster (2008), followed by the Model Y, Model 3, and subsequent models, reshaped the EV industry. Companies like Nissan (Leaf) and Chevrolet (Bolt) also contributed to the market’s expansion.

Advancements in Charging Technologies
- Level 2 Chargers: Introduced for faster home and public charging.
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): Tesla Superchargers, CCS, and CHAdeMO networks significantly reduced charging times.
- Wireless Charging: Emerging technology allows EVs to charge without plugging in.
- V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) Integration: EVs can now serve as energy storage units, supplying power back to the grid.
4. Future Trends in EV Technologies
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are expected to replace lithium-ion technology, offering:
- Faster charging times
- Higher energy density
- Longer lifespan
AI and Smart Charging Infrastructure
Artificial intelligence (AI) is improving EV efficiency by optimizing battery performance, predicting maintenance needs, and enhancing smart charging stations.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) Technology
V2X will enable communication between EVs and infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow and energy distribution.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells vs. Battery Electric Vehicles
While hydrogen fuel cells offer quick refueling times, battery EVs remain the dominant solution due to infrastructure and efficiency advantages.
5. The Role of Tayniu in Modern EV Charging Technologies
Portable & Smart Charging Solutions
Modern EV owners demand convenience and flexibility. Tayniu’s portable and home charging solutions enable users to charge their EVs efficiently, whether at home, work, or on the road.
- Fast-Charging Portable Chargers: Compact and efficient, perfect for travel.
- Smart Home EV Chargers: Optimized for energy efficiency and user control.
- Commercial Charging Stations: Scalable solutions for businesses and fleets.
As EV technologies continue evolving, having access to reliable charging solutions is crucial. Tayniu is committed to providing innovative, efficient, and safe charging options for EV users worldwide.
For more insights, check out Tayniu’s latest smart EV chargers.
6. EV Technologies Timeline: Key Innovations Over the Years
| Year | Key EV Technology Advancement |
|---|---|
| 1830s | First crude electric vehicle prototype |
| 1890s | Introduction of rechargeable batteries |
| 1900s | EVs peak in popularity |
| 1930s | EVs decline due to gasoline car dominance |
| 1990s | Lithium-ion battery breakthrough |
| 2008 | Tesla launches Roadster, EV revival |
| 2020s+ | Solid-state battery & AI smart charging |
Conclusion: What’s Next for EV Technologies?
The evolution of EV technologies has transformed electric vehicles from niche experiments to mainstream transportation solutions. With advancements in battery technology, AI-driven charging infrastructure, and vehicle-to-grid integration, the future of EVs is more promising than ever.
What do you think will be the next major breakthrough in EV technologies? Share your thoughts with us!
For more insights and cutting-edge EV charging solutions, explore Tayniu’s latest products.
Additional Resources on EV Technologies
- The Early History of Electric Cars – Smithsonian Magazine
- History of the Electric Car – U.S. Department of Energy
- Global EV Outlook – International Energy Agency
- Solid-State Batteries: The Next Big Leap – MIT Technology Review
- Electric Vehicle Battery Price Trends – BloombergNEF
- Supercharging Explained – Tesla
- The Combined Charging System (CCS) – CharIN
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology – U.S. Department of Energy
- The Future of Mobility and EV Market Trends – McKinsey & Company
- The Future of Electric Vehicles and Energy Transition – World Economic Forum
Last Updated on March 4, 2025 by tayniu