Level 2 vs. DC Fast Chargers: What’s Best for Your Business?
As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to grow, businesses are increasingly considering the installation of EV charging stations to cater to the needs of their customers and employees. The two primary types of EV charging solutions available for commercial use are Level 2 chargers and DC Fast Chargers. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand their differences and suitability for various business scenarios.
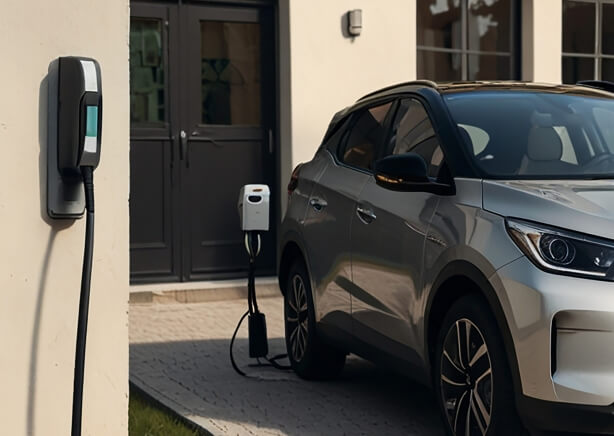

Level 2 Chargers
Overview:
Level 2 chargers are medium-speed chargers that operate at 240 volts and provide a reliable, moderate-speed charge. They are well-suited for scenarios where vehicles remain parked for extended periods, such as at workplaces, multifamily housing, or retail locations.
Key Specifications:
- Power Output: 3–19 kW
- Hardware Cost: $500–2,500 per port for commercial-grade units
- Installation Cost: $400–1,800 for basic installations (when existing electrical capacity is sufficient)
- Charge Time: 4–10 hours to charge a 60 kWh battery to 80%
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Lower upfront capital expenditure and minimal operating costs.
- Grid-Friendly: Rarely triggers demand charges or requires utility service upgrades.
- Battery Health: Lower current means minimal heat generation, resulting in less than 2% annual battery capacity degradation in most conditions.
- Scalability: Smart charging systems can distribute available power across multiple vehicles, maximizing existing electrical infrastructure.
Limitations:
- Slow Charging Speed: Not suitable for quick turnaround scenarios.
- Limited Utility for Road Trips: Impractical for long-distance travel support.
Ideal Applications:
- Residential settings (single-family homes and multi-unit dwellings)
- Workplaces where employees park for 8+ hours
- Hotels and overnight accommodations
- Fleet depots with predictable overnight dwell times
- Educational institutions and hospitals
DC Fast Chargers
Overview:
DC Fast Chargers (DCFC) are high-speed chargers designed for rapid charging in under an hour. They are ideal for businesses prioritizing speed and catering to drivers on tight schedules.
Key Specifications:
- Power Output: 50–350 kW
- Charge Time: Provides 80% charge in 20–60 minutes, depending on the battery size and charger power
- Hardware Cost: Significantly higher than Level 2 chargers
- Installation Cost: Requires advanced electrical infrastructure, including transformers and higher-capacity power lines
Advantages:
- Convenient for Drivers: Provides a fast recharge, making it ideal for quick stops.
- High-Traffic Locations: Suitable for highway rest stops, gas stations, and other high-traffic areas.
- Operational Flexibility: Particularly beneficial for industries using electric forklifts, yard tractors, or other heavy-duty vehicles.
Limitations:
- Higher Installation Costs: Requires significant investment in electrical infrastructure.
- Maintenance Costs: Higher due to the complexity of the system.
- Battery Lifespan: Fast charging can impact a battery’s lifespan.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all EVs come with a fast charging port.
Ideal Applications:
- Rest stops
- Gas stations
- Grocery stores
- Commercial hubs with quick turnovers
- Locations with available 480-volt power
- Commercial/industrial facilities with EV fleet initiatives
Choosing the Right Charger for Your Business
When deciding between Level 2 and DC Fast Chargers, consider the following factors:
1. Dwell Time: How long do vehicles typically stay parked at your location? For short stops, DC fast charging is ideal. For longer stays, Level 2 charging suffices.
2. Target Audience: Highway travelers or heavy-duty fleet operators prefer fast charging. Residents, employees, and shoppers may favor Level 2 chargers for convenience and affordability.
3. Space and Infrastructure: DC fast chargers require more space and a robust power supply. Ensure your property can accommodate the necessary infrastructure before deciding.
4. Budget and ROI: Evaluate upfront costs, operating expenses, and potential revenue streams from charging services.
5. Future-Proofing: Choose a charger that can be easily upgraded or is compatible with a wide range of EV models.
Conclusion
Both Level 2 and DC Fast Chargers offer unique benefits tailored to specific business needs. Level 2 chargers are cost-effective, versatile, and ideal for locations where vehicles remain parked for extended periods. DC Fast Chargers, on the other hand, deliver unmatched speed and convenience, making them indispensable for high-traffic or time-sensitive applications. In many cases, a combination of Level 2 and DC Fast Chargers provides the best of both worlds, offering flexibility to meet diverse charging demands. By aligning your charging infrastructure with your business goals, you can attract EV drivers, boost revenue, and contribute to a sustainable future.
Last Updated on May 26, 2025 by tayniu